Model: Seagate 600 SSD 240GB Solid State Drive
Manufacturer: Seagate
Provided By: Seagate
Seagate has been a leader in the storage industry for more than 30 years. Beginning with the industry's first 5.25-inch hard drive, the company has lead the way, growing to become one of the world's largest manufacturers of storage products. Seagate currently manufactures a wide range of products for both consumer and enterprise applications. Along with internal and external hard drives for the mobile and desktop markets, it offers a growing number of solid state and hybrid drives.
Earlier this year, Seagate introduced its first client solid state drive, the 600 SSD. Available in both 7mm and 5mm z-heights, the 600 SSD is the ultimate laptop upgrade for road warriors, power users, executives and gamers. With no moving or mechanical parts, this drive is more rugged and shock-resistant than standard hard drives. The 600 SSD also combines Link A Media Devices' (LAMD) LM87800 controller with Toshiba's 19nm Toggle mode MLC NAND flash to deliver faster boot up speeds, shorter application load times and improved system responsiveness.
The 600 SSD is available in 120GB, 240GB and 480GB capacities. For this review, Seagate sent us the 240GB version of the drive which is capable of delivering up to 550 MB/s sequential read and 450 MB/s sequential write speeds as well as up to 80,000 random read and 70,000 random write IOPS.
| Seagate 600 SSD 240GB Solid State Drive | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General Specifications
Performance
Power Consumption
Environment and Reliability
Dimensions and Weight
Other Features
|
Needless to say, this is only a taste of what the 600 SSD has to offer. To give you an idea of what to expect, we'll take a closer look at Seagate's new consumer SSD and then see how well it performs. Does the 600 SSD have what it takes? Can it deliver the performance and features that we've come to expect from Seagate? Keep reading as we find out.

Seagate does not currently offer the 600 SSD as part of a retail kit. If you buy the drive from a retailer like Amazon or Newegg, it will come in a sealed, antistatic bag. As with most other OEM, or bulk, packaged drives, it doesn't come with any documentation or extras like an adapter bracket or mounting screws.
Physical Features:
Like Seagate's other storage products, the 600 SSD is very well constructed. The top of the outer casing is made out of metal and is covered by a durable, matte black finish. The bottom of the casing is also made out of metal but is much thinner and is held in place using clips rather than screws. The sticker on the bottom shows the drive's part number, capacity and serial number.


The 600 SSD is the first client SSD available in both 7mm and 5mm z-heights. Where the 7mm version is best suited for desktop and laptop computers, the 5mm version is ready for the next generation of ultrabooks and tablets.
Like Seagate's 600 Pro SSD, the 600 SSD uses a Link_A_Media Devices (LAMD) LM87800 controller. The LM87800 features two ARM cores and supports up to 8 NAND channels, variable over-provisioning and LAMD's own eBoost technology, which significantly enhances the endurance of NAND flash.

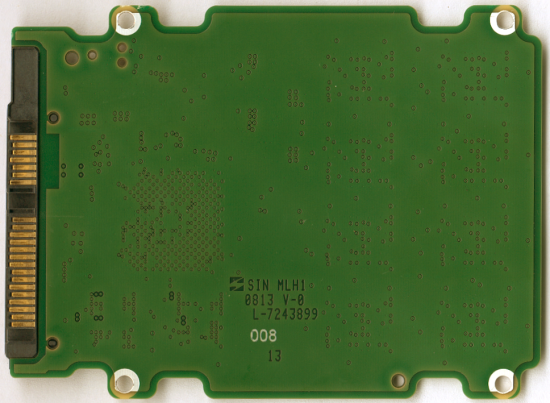
For the 240GB version of the 600 SSD, Seagate opted to use Toshiba's 32GB 19nm TH58TEG8DDJBA8C Toggle Mode NAND flash chips. Looking at the picture above, you can see that there are eight of these chips on the top of the PCB. The drive also has two 128MB Micron DDR2-800 memory chips that are used for caching.
The test system used in this review was an HP 8200 Elite. The computer came equipped with an Intel Core i5-2400 CPU, 4GB of DDR3 1333MHz memory, Seagate Barracuda 7200.12 ST3250312AS 250GB SATA 6 Gb/s hard drive, NVIDIA Quadro FX580 512MB PCIe graphics card and an Intel 82579-LM gigabit network card. For the operating system, I installed a fresh copy of Windows 7 Enterprise.
To test the performance of the Seagate 600 SSD, I ran a series of benchmarks using CrystalDiskMark 3.0.1, HD Tach RW 3.0.4.0, ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46, AS SSD, HD Tune Pro 4.61, Anvil's Storage Utilities and Iometer. For comparison, I've also included test results from the SanDisk Extreme II, OCZ Vector, Plextor PX-256M5Pro Xtreme, Samsung SSD 840 Pro, Samsung SSD 840, Kingston Ultra Plus, OCZ Vertex 4, OCZ Agility 4, Kingston SSDNow V300, Kingston HyperX 3K and SanDisk Extreme.

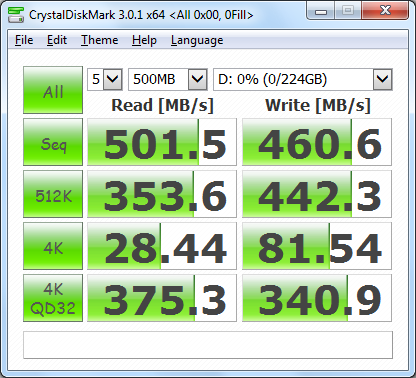
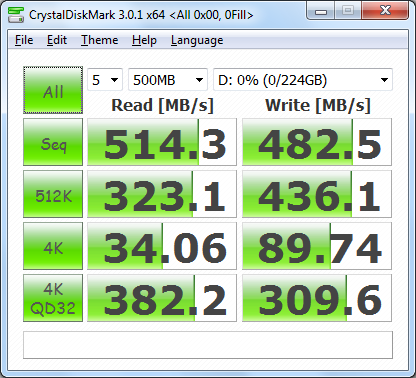
As I mentioned earlier, Seagate's 600 SSD is based on Link-a-Media's LM87800 controller chip. Looking at the screenshot above, you can see that it performs equally well with both incompressible (0%) and compressible (100%) data.
CrystalDiskMark 3.0.1:
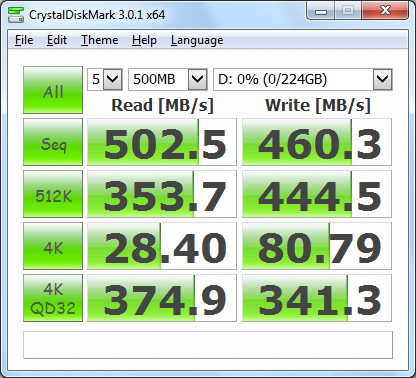
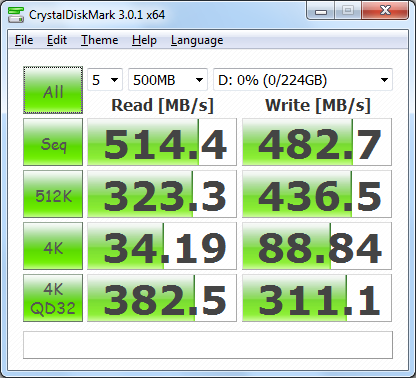
First, I ran a few quick tests using CrystalDiskMark. This benchmark tool measures the performance of a storage device by testing its sequential read and write speeds as well as its random read and write speeds using blocks 512K and 4K in size.
According to Seage, the 240GB 600 SSD is capable of reading at 550 MB/s and writing at 450 MB/s when connected to a SATA 6 Gb/s port. While the drive performed better than expected when writing, it came up a bit short in CrystalDiskMark's sequential read speed test.
The 600 SSD performed equally well when using highly compressible 0x00 (0 Fill) data. This time around, the drive was able to read at 501.5 MB/s and write at 460.6 MB/s.
HD Tach RW 3.0.4.0:
Next, I used HD Tach to test the 600 SSD's read, write and burst speeds as well as its seek times and CPU usage.
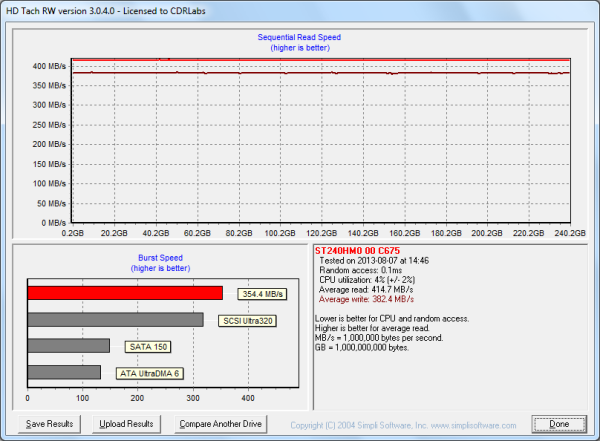
Looking at the screenshot above, you can see that the 600 SSD had average read and write speeds of 414.7 MB/s and 382.4 MB/s respectively, as well as a burst speed of 354.4 MB/s.
ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46:
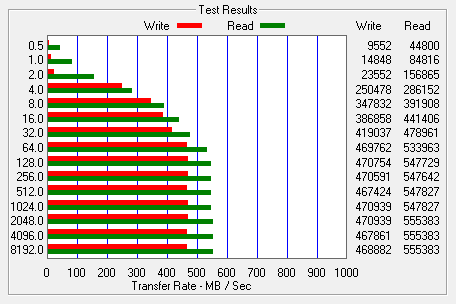
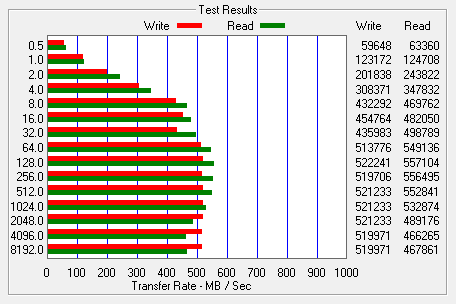
I also used ATTO Disk Benchmark to test the 600 SSD's sequential read and write speeds. The tests are run using blocks ranging in size from 0.5KB to 8192KB and the total length set to 256MB.
When tested with ATTO, the 600 SSD's read speeds topped out at about 555 MB/s and its write speeds at 470 MB/s.
AS SSD:
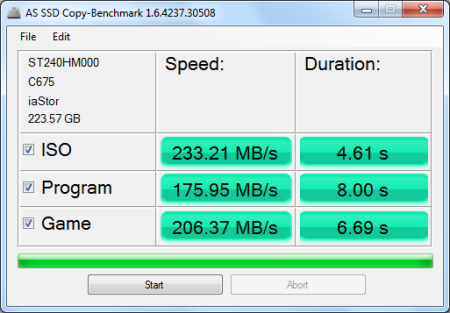
AS SSD is a relatively new benchmark designed specifically for solid state drives. The application contains five synthetic tests used to determine the sequential and random read and write performance of a drive.
AS SSD also includes a copy benchmark. This test copies an ISO (two large files), program (many small files) and game (small and large files), returning the speed and duration of each.
HD Tune Pro 4.61:
Next, I ran a series of tests using HD Tune Pro. This hard disk utility measures a drive's performance by testing its sequential read and write speeds as well as its access time, burst rate and CPU usage. For this review, I'm also going to use it to benchmark the 600 SSD's random read and write speeds, random access times and the number of operations per second.
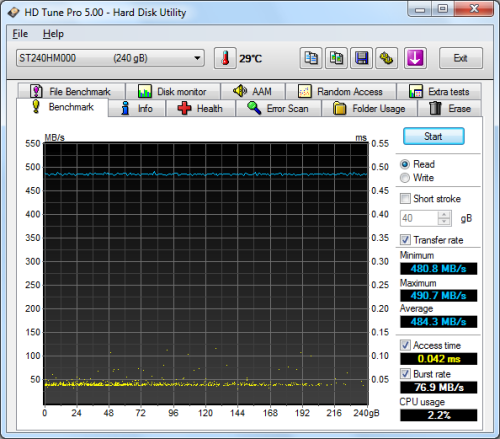 Seagate 600 SSD 240GB - HD Tune Read Benchmark |
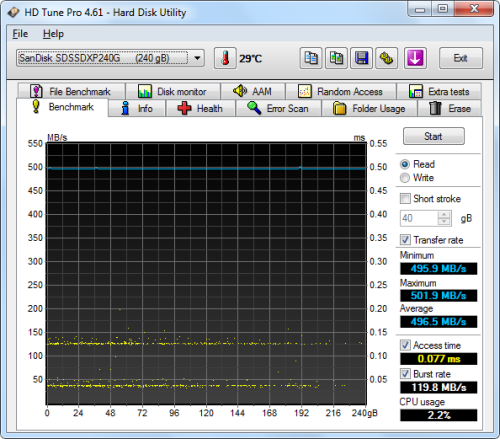 SanDisk Extreme II SSD 240GB - HD Tune Read Benchmark |
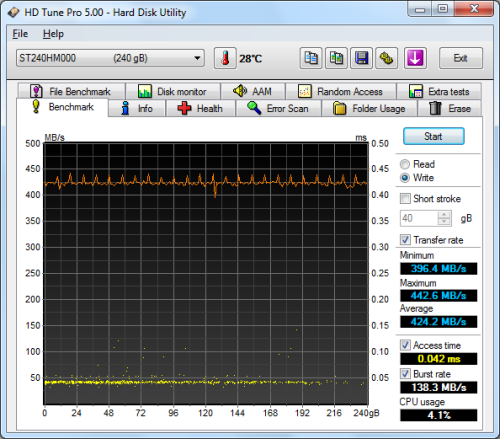 Seagate 600 SSD 240GB - HD Tune Write Benchmark |
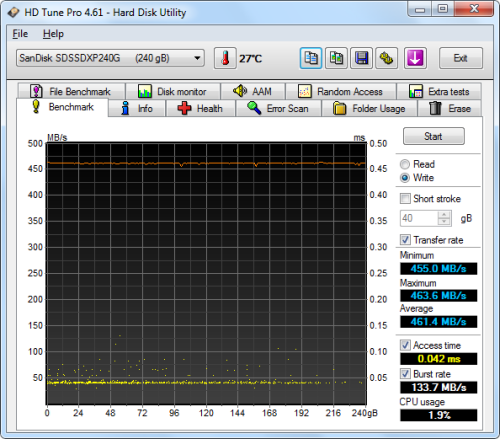 SanDisk Extreme II SSD 240GB - HD Tune Write Benchmark |
The 600 SSD performed very well when benchmarked with HD Tune. The drive had average read and write speeds of 484.3 MB/s and 424.2 MB/s, respectively, and a burst rate of 138.3 MB/s when writing
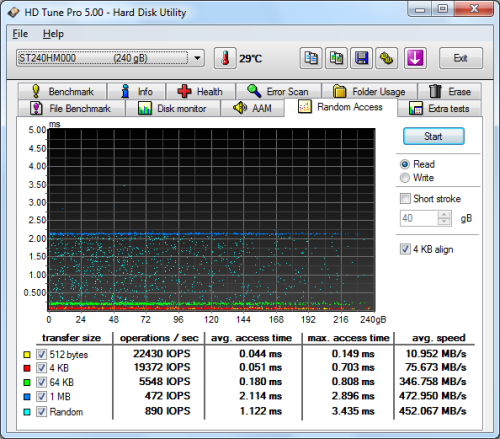 Seagate 600 SSD 240GB - HD Tune Random Access Read |
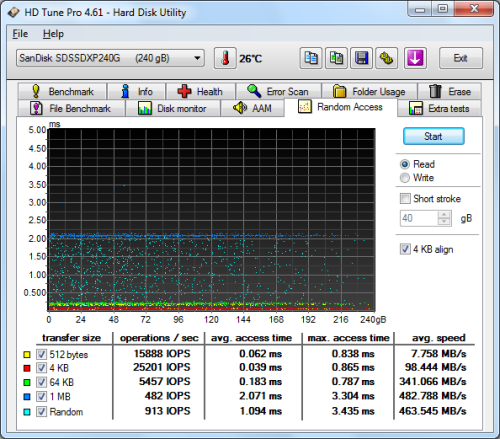 SanDisk Extreme II SSD 240GB - HD Tune Random Access Read |
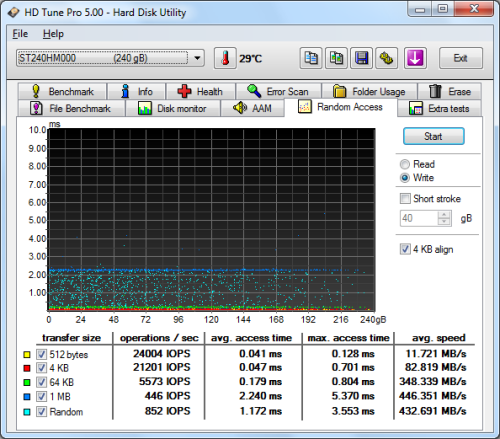 Seagate 600 SSD 240GB - HD Tune Random Access Write |
 SanDisk Extreme II SSD 240GB - HD Tune Random Access Write |
The 600 SSD didn't disappoint when doing random reads and writes. When reading 4KB blocks, the drive reached 19,372 IOPS and had an average speed of 75.673 MB/s. The 600 SSD was even faster when writing, reaching 21,201 IOPS with an average speed of 82.819 MB/s.
Anvil's Storage Utilities:
Anvil's Storage Utilities is another new benchmark designed with SSDs in mind. The standard storage benchmark measures a drive's performance by testing its transfer speeds, access times and IOPS.

Iometer:
Lastly, I ran a series of tests using Iometer. This tool can be configured to benchmark a number of things. In this case, I used it to measure the Seagate's read and write speeds and the number of operations per second. The tests were run using random bytes and a queue depth of 3.

The 600 SSD's performance was very similar to what we saw in our other tests. The drive was able to read at 484.58 MB/s and write at 448.61 MB/s.

The 600 SSD also performed pretty well when doing random reads and writes. In our tests, the drive was able to read at 141.88 MB/s and write at 293.97 MB/s.

According to Seagate, the 240GB version of the 600 SSD is capable of 80,000 IOPS when reading and 70,000 IOPS when writing 4K blocks. In our tests, the drive reached 36,322 random read IOPS and 75,256 random write IOPS. The only way I was able to reach 80,000 random read IOPS was to increase the queue depth. With the queue depth set to 32, the SSD 600 reached 91,439 random read IOPS and 83,192 random write IOPS.
TRIM Performance:
While SSD's offer many benefits, there are some downsides to using flash memory. One of the biggest issues people run into is performance degradation. Over time, an SSD will run out of fresh blocks and will have to write over data the file system has marked as deleted. This procedure is very complicated and can slow an SSD's write speeds considerably.
To fix this problem, most manufacturers have added TRIM support to their SSDs. The TRIM command allows an operating system, such as Windows 7, to tell an SSD which data blocks are no longer in use. Using this information, the drive pro-actively erases these blocks and adds them to the free block pool.

To test the 600 SSD's TRIM function, I first put the drive in a "dirty" state. I used Iometer to fill the entire drive and then ran a random write test for 30 minutes. This had very little effect on the 600 SSD's read speed. However, its average write speed dropped to 76.2 MB/s.
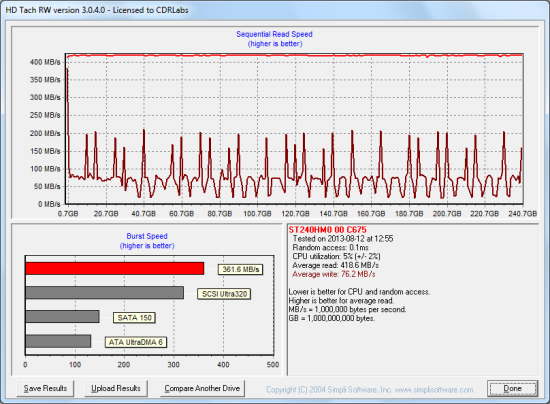
Seagate 600 SSD - Dirty
To see how well the 600 SSD could recover, I let the computer sit for about two and a half hours and then reran the test. The drive wasn't able to reach the factory fresh performance shown in our earlier tests. However, its average write speed climbed up to 189.0 MB/s.

Seagate 600 SSD - After TRIM
Lastly, I used Parted Magic to perform a secure erase on the 600 SSD. With the drive wiped clean, it had average read and write speeds of 413.6 MB/s and 392.3 MB/s, respectively.
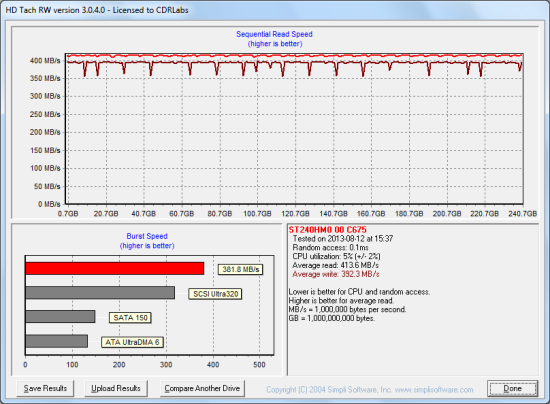
Seagate 600 SSD - Secure Erase
Final Thoughts:
With the 600 SSD, Seagate has made its long awaited entrance into the consumer solid state drive market. This thin, yet rugged, drive combines Link A Media Devices' (LAMD) LM87800 controller with Toshiba's 19nm Toggle mode MLC NAND flash to deliver a fast and responsive computing experience. In our sequential read and write tests, the 600 SSD was able to read at speeds as high as 555 MB/s and write at speeds in excess of 460 MB/s. It also did reasonably well our random write tests, producing more than 75,000 IOPS at low queue depths. Increasing the queue depth did lead to better results. However, the 600 SSD still had a hard time keeping up with drives like the Samsung 840 Pro.
Samsung's 600 SSD is available now in 120GB, 240GB and 480GB capacities. Prices on Amazon.com currently range from $110 up to $410, with the 240GB version reviewed here going for about $210.
Highs:
- Available in 120GB, 240GB and 480GB capacities
- Link A Media Devices (LAMD) LM87800 controller
- Good sequential and random read and write performance
- Performs equally well with compressible and incompressible data
- Rugged, ultra-slim design
- SATA 6Gb/s interface
- Toggle Mode NAND flash
- Large DRAM cache
- Supports TRIM, SMART and NCQ
- Available in both 7mm and 5mm z-heights
- Reasonably priced
- 3 year warranty
Lows:
- OEM packaging does not include any accessories
- Does not support hardware based encryption