Model: AMD Radeon R7 240GB Solid State Drive
Manufacturer: OCZ Storage Solutions
Provided By: OCZ Storage Solutions
As one of the biggest names in the computer industry, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) doesn't need much of an introduction. Founded in 1969, the company got its start by producing logic chips. As time went on, AMD expanded into the microprocessor market, serving first as a second source for Intel before introducing its own line of x86-compatible processors. Today, AMD is the world's second largest manufacturer of microprocessors. Along with a wide range of processors for the desktop and mobile markets, the company currently offers graphics cards, motherboard chipsets and memory kits.
AMD recently partnered with OCZ to launch the company's first solid state drive, the Radeon R7. Designed with gamers and graphics-hungry power users in mind, the Radeon R7 is based on OCZ's Indilinx-infused Barefoot 3 M00 controller. This cutting-edge controller is powered by both an ARM Cortex processor and OCZ's own Aragon co-processor and features an advanced, multi-level ECC engine, low write amplification, efficient garbage collection and adaptive flash management algorithms. The Radeon R7 is also equipped with up to 480GB of Toshiba's latest Advanced 19nm (A19) MLC NAND flash. Along with 30GB of host writes per day, the drive is capable of 550MB/s read and 530MB/s write speeds and a maximum of 90,000 4KB random write IOPS.

For this review, OCZ sent us the 240GB version of the Radeon R7. This SSD comes equipped with 512MB of on-board cache and is capable of delivering up to 550 MB/s sequential read and 530 MB/s sequential write speeds as well as up to 95,000 random read and 90,000 random write IOPS.
| AMD Radeon R7 240GB Solid State Drive | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General Specifications
Performance
Reliability
Power Consumption
Environmental
Dimensions and Weight
Other Features
|
Needless to say, this is only a taste of what the Radeon R7 has to offer. To give you an idea of what to expect, we'll take a closer look at AMD's new SSD and then see how well it performs. Does the Radeon R7 have what it takes? Can it deliver the performance and features that we've come to expect from AMD? Keep reading as we find out.
The Radeon R7 comes in a small, black and red box. While there aren't a lot of details on the front, the back of the box advertises many of the drive's key features including its SATA 6Gbps interface, 2.5" ultra-slim form factor, MLC flash memory, TRIM support and AES 256-bit encryption. Inside the box you'll find the SSD, a 3.5" adapter bracket, mounting screws, installation guide, download instructions and serial number for Acronis True Image and a small sheet of paper with information on how to reach OCZ's tech support.

Physical Features:
The construction of the Radeon R7 is very similar to that of OCZ's Vector 150 and Vertex 460 SSDs. The outer casing is made out of an aluminum alloy and is covered by a special black anodized finish. The top of the drive also has a large, black and red sticker showing that it is part of AMD's Radeon series of solid state drives.


Like the Vector and Vector 150, the Radeon R7 uses the Indilinx Barefoot 3 M00 (IDX500M00-BC) controller chip. Designed entirely in-house, the Barefoot 3 M00 is powered by an ARM Cortex processor as well as OCZ's own Aragon co-processor.


For the 240GB Radeon R7, OCZ opted to use Toshiba's A19nm TH58TEG7DDKBA4C MLC NAND flash modules. Looking at the pictures above, you can see that there are eight of these 16GB NAND flash packages on either side of the PCB. The drive also has two 256MB Micron 3KK77 D9PSH DDR3 SDRAM memory chips that are used for caching and garbage collection.
The test system used in this review was an HP 8200 Elite. The computer came equipped with an Intel Core i5-2400 CPU, 4GB of DDR3 1333MHz memory, Seagate Barracuda 7200.12 ST3250312AS 250GB SATA 6 Gb/s hard drive, NVIDIA Quadro FX580 512MB PCIe graphics card and an Intel 82579-LM gigabit network card. For the operating system, I installed a fresh copy of Windows 7 Enterprise.
To test the performance of AMD's 240GB Radeon R7 SSD, I ran a series of benchmarks using CrystalDiskMark 3.0.3, HD Tach RW 3.0.4.0, ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46, AS SSD, HD Tune Pro 4.61, Anvil's Storage Utilities and Iometer. For comparison, I've also included test results from the Silicon Power Slim S80, Samsung SSD 850 EVO, OCZ ARC 100, SanDisk Ultra II, Crucial MX100, SanDisk Extreme Pro, Samsung SSD 850 PRO, Plextor PX-256M6S, Toshiba Q Series Pro, Plextor PX-256M6M, Samsung SSD 840 EVO mSATA, OCZ Vector 150, OCZ Vertex 450, Silicon Power Slim S55, Samsung SSD 840 EVO, Seagate 600 SSD, SanDisk Extreme II, Plextor PX-256M5M, OCZ Vector, Plextor PX-256M5Pro Xtreme, Samsung SSD 840 Pro and Samsung SSD 840.

Like OCZ's Vector 150 SSD, the AMD Radeon R7 SSD is based on the Indilinx Barefoot 3 M00 controller platform. Looking at the screenshot above, you can see that, unlike SandForce controllers, it performs equally well with both incompressible (0%) and compressible (100%) data.
CrystalDiskMark 3.0.3:
First, I ran a few quick tests using CrystalDiskMark. This benchmark tool measures the performance of a storage device by testing its sequential read and write speeds as well as its random read and write speeds using blocks 512K and 4K in size.
According to AMD, the 240GB Radeon R7 is capable of reading at 550 MB/s and writing at 530 MB/s when connected to a SATA 6 Gb/s port. While the drive performed well, it came up a bit short of these numbers in CrystalDiskMark's sequential read and write speed tests.
The Radeon R7 performed equally well when using highly compressible 0x00 (0 Fill) data. This time around, the drive was able to read at 469.2 MB/s and write at 485.5 MB/s.
HD Tach RW 3.0.4.0:
Next, I used HD Tach to test the Radeon R7's read, write and burst speeds as well as its seek times and CPU usage.

AMD Radeon R7 240GB
Looking at the screenshot above, you can see that the Radeon R7 had average read and write speeds of 300.8 MB/s and 305.6 MB/s respectively, as well as a burst speed of 338.7 MB/s.
ATTO Disk Benchmark 2.46:
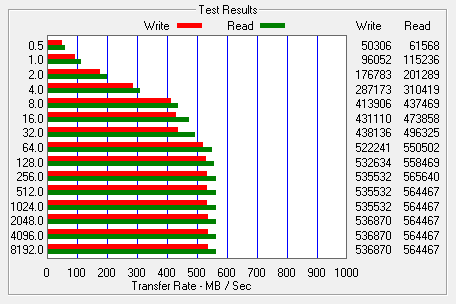
I also used ATTO Disk Benchmark to test the Radeon R7's sequential read and write speeds. The tests are run using blocks ranging in size from 0.5KB to 8192KB and the total length set to 256MB.
When tested with ATTO, the Radeon R7's read speeds topped out at about 557 MB/s and its write speeds at 532 MB/s.
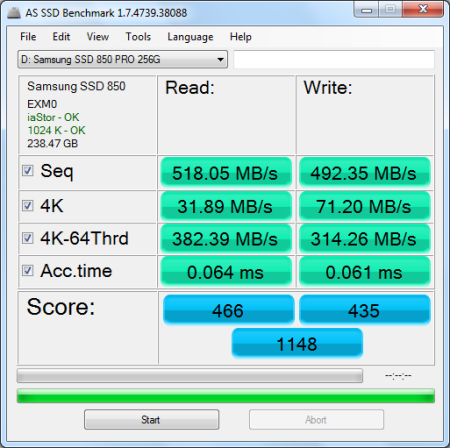
AS SSD:
AS SSD is a relatively new benchmark designed specifically for solid state drives. The application contains five synthetic tests used to determine the sequential and random read and write performance of a drive.
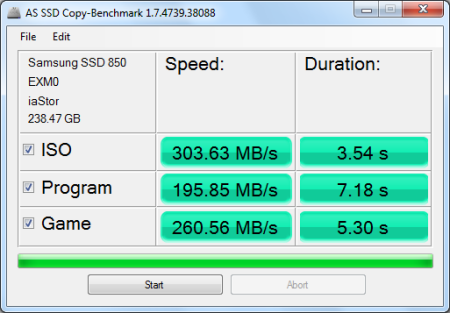
AS SSD also includes a copy benchmark. This test copies an ISO (two large files), program (many small files) and game (small and large files), returning the speed and duration of each.
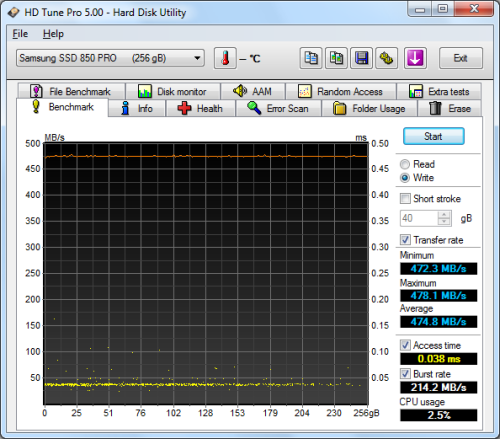
HD Tune Pro 5.00:
Next, I ran a series of tests using HD Tune Pro. This hard disk utility measures a drive's performance by testing its sequential read and write speeds as well as its access time, burst rate and CPU usage. For this review, I'm also going to use it to benchmark the Radeon R7's random read and write speeds, random access times and the number of operations per second.
The Radeon R7 didn't do as well as I had expected when benchmarked with HD Tune. The drive had average read and write speeds of 287.1 MB/s and 345.8 MB/s, respectively, and a burst rate of 354.5 MB/s when reading.
The Radeon R7 didn't disappoint when doing random reads and writes. When writing 4KB blocks, the drive reached 19,271 IOPS and had an average speed of 75.281 MB/s. The Radeon R7 was slightly faster when reading, reaching 19,543 IOPS with an average speed of 76.343 MB/s.
Anvil's Storage Utilities:
Anvil's Storage Utilities is another new benchmark designed with SSDs in mind. The standard storage benchmark measures a drive's performance by testing its transfer speeds, access times and IOPS.

Iometer:
Lastly, I ran a series of tests using Iometer. This tool can be configured to benchmark a number of things. In this case, I used it to measure the Radeon R7's read and write speeds and the number of operations per second. The tests were run using random bytes and a queue depth of 3.

The Radeon R7's performance was very similar to what we saw in our other tests. The drive was able to read at 524.02 MB/s and write at 431.76 MB/s.

The Radeon R7 wasn't one of the faster drives we've tested when it came to random reads and writes. In our tests, the drive was able to read at 104.30 MB/s and write at 214.83 MB/s.

According to AMD, the 240GB Radeon R7 is capable of 95,000 IOPS when reading and 90,000 IOPS when writing 4K blocks. In our tests, the drive reached 26,702 random read IOPS and 54,998 random write IOPS. The only way I came close to OCZ's numbers was to increase the queue depth. With the queue depth set to 32, the Radeon R7 reached 91,581 random read IOPS and 81,070 random write IOPS.
TRIM Performance:
While SSD's offer many benefits, there are some downsides to using flash memory. One of the biggest issues people run into is performance degradation. Over time, an SSD will run out of fresh blocks and will have to write over data the file system has marked as deleted. This procedure is very complicated and can slow an SSD's write speeds considerably.
To fix this problem, most manufacturers have added TRIM support to their SSDs. The TRIM command allows an operating system, such as Windows 7, to tell an SSD which data blocks are no longer in use. Using this information, the drive pro-actively erases these blocks and adds them to the free block pool.

To test the Radeon R7's TRIM and garbage collection functions, I first put the drive in a "dirty" state. I used Iometer to fill the entire drive and then ran a random write test for 30 minutes. Looking at the screenshot below, you can see that the Radeon R7's average read and write speeds dropped to 240.0 MB/s and 102.8 MB/s, respectively.

OCZ Radeon R7 - Dirty
I let the computer sit for a couple of hours and then reran the test. The drive's average write speed jumped back up to 232.1 MB/s. However, its average read speed dropped down to 236.6 MB/s while it was recovering.

OCZ Radeon R7 - After TRIM
Lastly, I used the Radeon Toolbox utility to perform a secure erase on the Radeon R7. With the drive wiped clean, it had average read and write speeds of 295.1 MB/s and 257.4 MB/s, respectively.

OCZ Radeon R7 - Secure Erased
Final Thoughts:
With the Radeon R7, AMD has made its long awaited entrance into the consumer solid state drive market. The result of a partnership between AMD and OCZ, this good looking, ultra-slim drive combines the Indilinx-infused Barefoot 3 M00 controller with Toshiba's latest A19nm MLC NAND flash to deliver a good mix of performance, endurance and value. In our sequential read and write tests, the 240GB version of the Radeon R7 was able to read at speeds as high as 552 MB/s and write at speeds in excess of 485 MB/s. It also did reasonably well in our random write tests, producing almost 55,000 IOPS at low queue depths. As you'd expect, the Radeon R7 performed better at higher queue depths. However, it still had a hard time keeping up with some of the higher priced, enthusiast-oriented SSDs like OCZ's own Vector 150 and Samsung's 850 PRO.
Despite its many strengths, OCZ's Barefoot 3 controller has been around for a few years now and is starting to get a bit long in the tooth. Where the latest controllers from Marvell and Samsung offer support for Device Sleep (DEVSLP) mode and self-encrypting drive (SED) technologies that are TCG Opal 2.0 and eDrive compliant, the Barefoot 3 does not. Given, this probably isn't an issue if you're looking for an SSD for your gaming rig. However, these are things you may want to consider if the Radeon R7 is going in a laptop or you're in a situation where data security is a concern.
The Radeon R7 is available now in 120GB, 240GB and 480GB capacities. Prices on Amazon currently range from $85 up to $244, with the 240GB version reviewed here going for about $130.

Highs:
- Available in 120GB, 240GB and 480GB capacities
- Endurance rated at 30GB/day for 4 years
- Good sequential and random read and write performance
- Performs equally well with compressible and incompressible data
- SATA 6Gb/s interface
- Toggle Mode MLC NAND flash
- Large DRAM cache
- Supports TRIM and idle background garbage collection
- Well constructed design
- AES 256-bit encryption
- Includes a 2.5" to 3.5" adapter bracket
- Includes Acronis True Image cloning software
- 4 year ShieldPlus warranty
Lows:
- Random write performance at low queue depths could be better
- Does not support DEVSLP
- Does not support TCG Opal or eDrive encryption